No company is afraid of the term credential leak. Or what does happen when your passwords or access tokens get online? The thing is that the majority of the breaches occur in the stages that can be predicted, and knowing them will allow you to prevent attackers before they get into your vital systems.
We can reverse engineer how a credential leak actually works out, and how you can disrupt that chain with early-warning intelligence of Vigile.
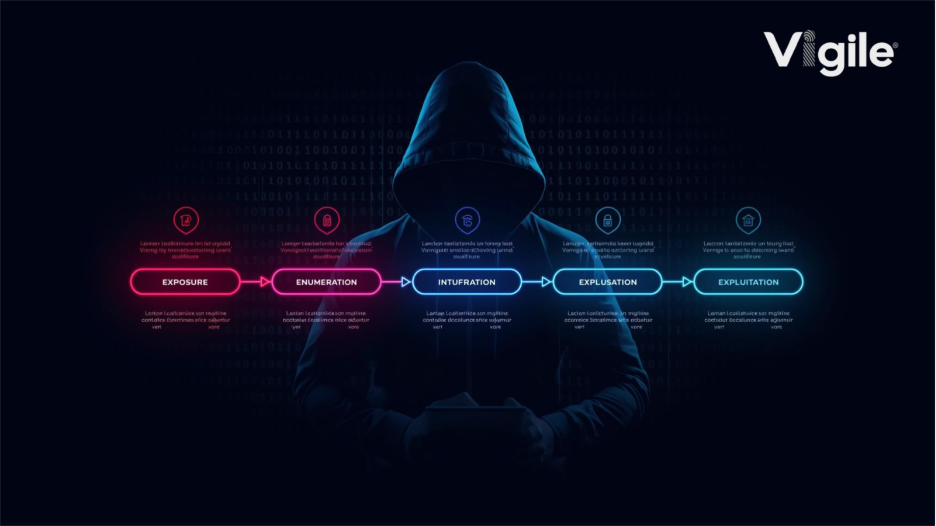
Stage 1: The Leak Surfaces
A credential leak is typically initiated with a minor detail:
- An employee who is phished provides log-in information.
- An infostealer virus collects passwords saved on the browser.
- One of the third-party vendors is hacked and your logins are included in their records.
Such stolen credentials are then sold off or put together in breach databases in the dark web. At this point, even the burglars do not have to break in; they just sell your access like money.
Stage 2: Testing the Keys
After spreading credentials, hackers start enumerating users, attempting usernames and passwords on various victims.
- They carry out credential stuffing on company portals, VPNs, or email services.
- They verify variability (for example, Welcome2025!, Welcome2026!).
- They use bots to automate the process, which can also check thousands of combinations in a minute.
This is where the initial unauthorized access usually occurs in case your company does not have multi-factor authentication (MFA) or anomalous logins detection.
Stage 3: Intrusion: Gaining a Foothold
After a valid combination is found, the attacker gets into the system unobtrusively. They:
- Map internal systems to explore your network.
- Change privileges to administrator or root access.
- Install backdoors or stealth malware to remain persistent.
It is the silent phase where the majority of victims are not aware that a breach has taken place. The longer this stage lasts, the more harm may be caused.
Stage 4: Exfiltration: The Data Theft
Once the attacker has taken over, they start data exfiltration:
- Customer databases
- Source code repositories
- Confidential documents
- Financial records
The information is often compressed and encrypted and then uploaded to attacker-controlled servers, making it more difficult to detect. This information can be found within days on dark-web markets or can be used for extortion.
Stage 5: The Stage of Exploitation: The Aftermath
Lastly, the stolen credentials and data are weaponized.
- Ransomware activation and phishing are organized by attackers via legitimate corporate accounts.
- Threat actors or competitors can purchase the information to use in industrial espionage.
- Your business suffers loss of finances, damage to brand, and fines.
Credential leaks are not the least frequent root causes. According to the report Cost of a Data Breach by IBM, on average, a breach now costs over USD 4.7 million.
Breaking the Chain: Prevention Begins with Vigilance
You cannot prevent criminals from stealing data elsewhere, but you can prevent its use.
- Enforce credential continuous monitoring.
- Use good password hygiene and MFA.
- Uncover dark-web discussions concerning domains and accounts of employees.
- Create a response playbook to ensure that incidents are contained within hours rather than weeks.
How Vigile Assists You in Intercepting Credential Leaks
Vigile breach-intelligence platform monitors the dark web, infostealer logs, and leak forums to determine the exposed credentials prior to exploitation by the attackers. You get alerts in real-time, risk scoring, and immediate containment insight.
By Vigile, organizations change their roles from reactive victims to active defenders in the five stages of breaches.
Protect your team today. Visit vigile.ai to understand how Vigile can detect, monitor, and neutralize credential leakages before they cause harm.